The global economy is interconnected, presenting both opportunities and risks for investors. While the US market remains dominant, relying solely on it can be risky. Diversification is key, and the SPDR Portfolio Developed World ex-US ETF (SPDW) offers a compelling avenue for accessing developed markets outside the United States. But is SPDW the right choice for you? This article explores the advantages, disadvantages, and practical considerations for incorporating SPDW into your investment strategy.
Understanding SPDW Holdings: A Global Perspective
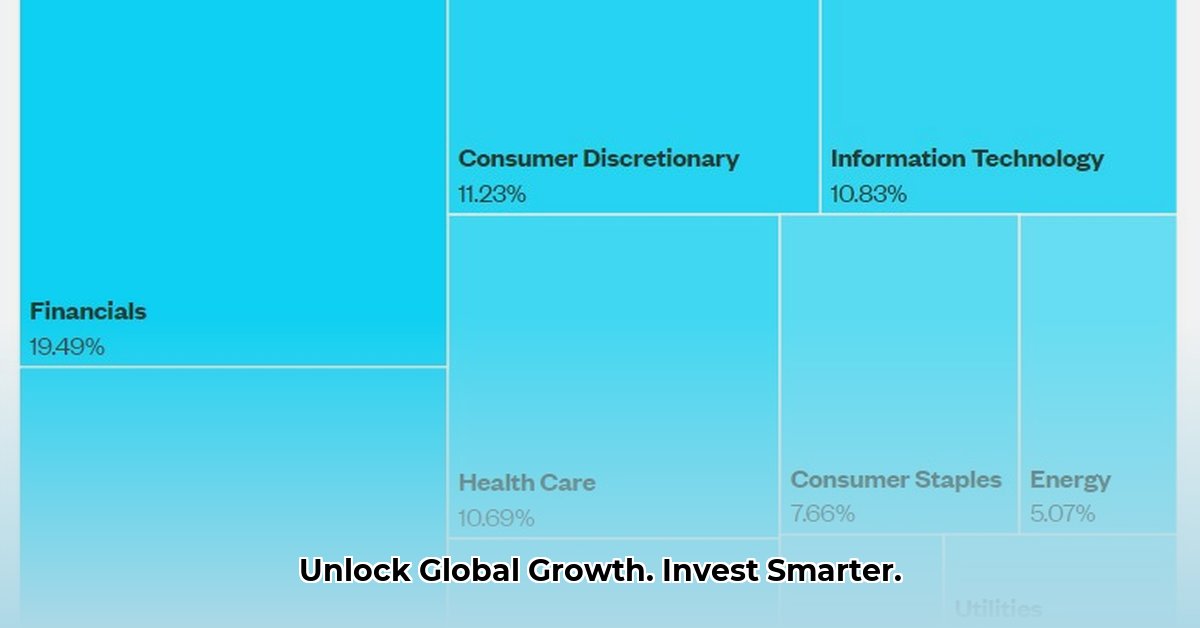
SPDW provides exposure to a broad range of companies in developed countries excluding the US. This diversification reduces reliance on a single national economy, strengthening your portfolio's resilience against localized economic downturns. Think of it as adding multiple sturdy towers to your financial castle, rather than relying on a single, potentially vulnerable structure. This approach is particularly relevant in today's volatile global environment. Did you know that the IMF projects [link to 2024 IMF economic outlook] significant variations in growth across developed nations this year?
SPDW's Advantages: A Balanced Approach
SPDW offers several compelling advantages:
- Diversification: Reduces risk by spreading investments across multiple countries and sectors. A downturn in one region won't necessarily sink your entire investment.
- Liquidity: Easy to buy and sell, providing flexibility for accessing your funds. This flexibility is crucial for navigating market uncertainty.
- Established Companies: Primarily invests in large, established companies, generally seen as more stable than smaller, emerging firms.
- Passive Management: Requires minimal active oversight, appealing to busy investors seeking a low-maintenance international investment strategy.
SPDW's Challenges: Navigating the Global Landscape
However, potential drawbacks must also be considered:
- Global Event Sensitivity: The ETF's performance is susceptible to international events, like political instability or economic crises in major economies.
- Currency Fluctuations: Shifts in exchange rates (e.g., USD/EUR) can heavily influence returns, potentially offsetting gains from underlying investments.
- Exclusion of Smaller Companies: Focusing on large caps potentially misses out on higher growth opportunities available through smaller, more dynamic companies.
- Passive Management limitations: While simple, this also means no active adjustments to mitigate unforeseen market downturns.
Is SPDW Right for Your Portfolio?
The suitability of SPDW depends on individual circumstances.
Individual Investors:
- Short-term: Not recommended due to market volatility and potential for short-term losses.
- Long-term: Suitable for those comfortable with moderate risk and seeking global diversification within a long-term investment strategy.
Financial Advisors:
SPDW can be a valuable tool for diversifying client portfolios, especially those with a longer-term outlook. However, careful consideration of currency hedging and the integration of SPDW into a broader investment plan is crucial. "Currency hedging should be a central part of the conversation when discussing international investments like SPDW," says Dr. Anya Sharma, PhD, CFA, Professor of Finance at the University of California, Berkeley.
Institutional Investors:
May use SPDW as a benchmark or a component of wider global investment strategies, requiring a detailed analysis of sector weightings and index-tracking efficiency.
Taking Action: A Step-by-Step Guide
To determine if SPDW fits your needs:
- Analyze Holdings: Scrutinize the ETF's holdings to identify potential risks and opportunities within specific companies and countries.
- Index Methodology: Understand the index's construction to identify any inherent biases or selection criteria.
- Comparative Analysis: Compare SPDW with similar international ETFs, focusing on expense ratios and risk-adjusted returns. "Expense ratios are often overlooked, but they can significantly impact long-term returns," notes Mr. David Chen, CFP, Managing Director at Chen Financial Advisors.
- Cost Assessment: Thoroughly evaluate the expense ratio, as even small differences can greatly affect long-term returns.
Mitigating Currency Risk in SPDW Investments
Understanding and addressing currency risk is essential. Strategies to mitigate this risk include:
- Currency Hedging: Employing financial instruments to offset potential exchange rate losses.
- Currency-Hedged ETFs: Investing in ETFs with built-in currency hedging mechanisms.
- Diversification: Combining SPDW with assets less sensitive to currency fluctuations.
Remember, the information provided is for educational purposes. Consult a financial professional for personalized advice before making investment decisions.
Key Takeaways
- SPDW offers a diversified approach to global investing outside the US market.
- Currency risk is a significant factor impacting SPDW's performance.
- Various strategies exist to mitigate currency-related risks.
- A long-term investment perspective, combined with a thorough risk assessment, is vital for success.